Ticks can transmit a variety of bacteria, parasites and viruses to humans. The most common tick-borne disease is Lyme disease. Other tick-borne illnesses include Babesia, Bartonella and Ehrlichia/Anaplasma. These illnesses are often Lyme disease coinfections.
Coinfections are quite common in those suffering from chronic Lyme disease. According to the Lyme disease organization’s website, the majority of people suffering from chronic Lyme disease have at least one coinfection, and as many as 30 percent suffer from two or more coinfections.
Lyme Disease
Borrelia, also known as Lyme disease, Southern Tick-Associated Rash Illness (STARI) or Masters’ Disease is transmitted by three ticks, including the deer tick, Pacific black-legged tick and the Lone Star tick. The symptoms of Lyme disease vary from person to person and depend on the length and severity of the infection. The most common symptoms include:
- Joint Pain
- Sweats
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
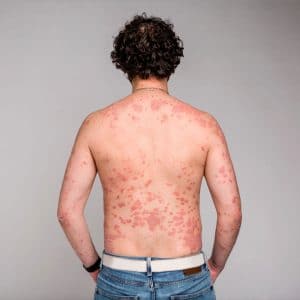
- A bull’s eye rash
If Lyme disease is not treated early, chronic and life-threatening symptoms can arise. Because the bacteria are found in the blood, it can affect different systems in the body causing a wide variety of symptoms. These include:
- Cardiovascular issues – heart murmur, chest pain, palpitations, valve prolapse and blockages in the heart
- Widespread pain throughout the body – sore throat, abdominal pain, pelvic pain, muscle pain, joint pain, neck pain and back pain
- Respiratory problems – shortness of breath, wheezing, respiratory infection, pneumonia and cough
- Digestive Issues – constipation, heartburn, diarrhea, GERD, nausea, vomiting
- Urinary problems – painful urination, frequent urination, an increased risk of urinary tract infections
- Vision Issues – blurry vision, light sensitivity, pain, decreased visual acuity, drooping eyelids, conjunctivitis and even blindness
- Hearing difficulties – sensitivity to noise, ear pain, hearing loss and tinnitus
- Neurological symptoms – Bells’ Palsy, seizures, stiff neck, facial twitching, coordination issues, poor reflexes, headaches, vertigo and meningitis
- Psychiatric symptoms – memory problems, irritability, mood swings, depression, sleep disturbances and disorientation
- Arthritis
- Enlarged spleen
- Pregnancy-related symptoms – premature births, stillborn, birth defects and miscarriages
Coinfections of Lyme Disease
In addition to causing Lyme disease, ticks can cause a variety of vector-borne illnesses. A vector-borne illness simply means an illness that is passed by ticks, fleas or mosquitos to humans from a variety of animals, including mice, squirrels, cats, dogs and livestock. A tick can carry a variety of bacteria, fungi, protozoans and viruses. These can be transmitted to a human in a single bite, causing a variety of tick-borne illnesses. These illnesses are called coinfections.
Babesia
Babesia, a parasitic infection much like malaria, attack the red blood cells throughout the body. Many people experience mild symptoms, such as high fevers and chills that can last for weeks or even months. As the illness progresses, you may experience a myriad of symptoms, including:
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Hip pain
- Headaches
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive sweating
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Reduced appetite
- Vomiting
- Depression
- and more
The symptoms listed above are generally mild; however, those who do not have a spleen, have a weakened immune system or are elderly may experience complications. These complications include:
- Liver problems, including liver failure
- Kidney failure
- Low blood pressure
- Hemolytic anemia
- Respiratory failure
- Heart failure
Bartonella
Bartonella is another tick-borne illness that mimics the symptoms of a number of bacterial infections. Many people refer to this illness as cat scratch fever because cats are carriers of the Bartonella bacteria. This bacterium can be transmitted to humans by a cat scratch, a cat bite or a flea. The symptoms of this infection include:
- A streaked rash resembling stretch marks
- Loss of appetite
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Swollen glands in the upper body, including head, neck and arms
In addition to the symptoms listed above, a person may experience neurological complications, including:
- Ataxia
- Tremors
- Blurred vision
- Memory loss
- Headaches
- Balance issues
- Numbness in the persons extremities
- Psychiatric manifestations, such as anxiety, depression, personality changes and panic attacks
Ehrlichia/Anaplasma
Unlike the other coinfections that are transmitted by the red blood cells, Ehrlichia and Anaplasma affect the white blood cells. This can cause an increased risk of infection and can cause:
- Sudden high fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
In elderly people or those with a weakened immune system, the symptoms of Ehrlichia/Anaplasma can become more severe and cause:
- Low blood platelet counts
- Low white blood cells
- Kidney failure
- Insufficient respiratory functions
- Elevated liver enzymes
Holistic Treatment for Lyme Disease Coinfections
Persons suffering from coinfections often experience more symptoms and those symptoms are generally more severe than the original infection. These coinfections are often difficult to diagnose because the symptoms often overlap one another.
Because of the variety of symptoms associated with tick-borne illnesses, it is essential that you get tested as soon as symptoms appear. With a proper diagnosis along with a holistic treatment for Lyme disease, you can fully recover from a tick-borne illnesses.