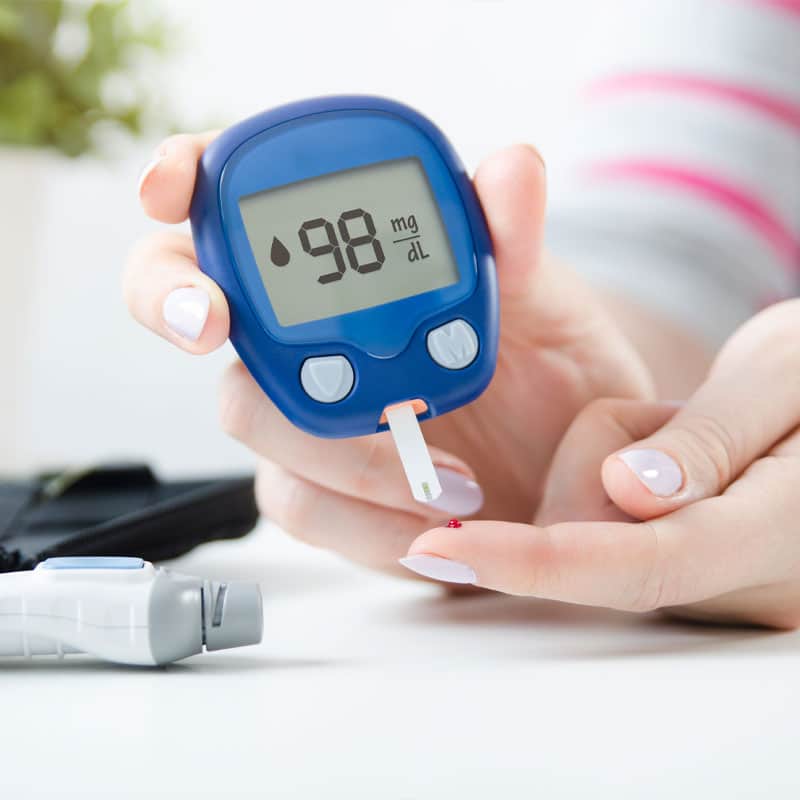
Approximately 10 percent of the US population have been diagnosed with diabetes across economic, ethnic, and social backgrounds. In addition, doctors have not yet diagnosed another 7.3 million people who have diabetes. Diabetes affects multiple systems throughout the body. It occurs when your pancreas does not produce enough insulin (type 1 diabetes) or cannot utilize insulin efficiently (type 2 diabetes or prediabetes). When the body cannot move glucose from the bloodstream to the cells in the body to use it as energy, your blood sugar becomes too high.
Symptoms of Diabetes
Early detection is vital to decreasing the risk of long-term complications, which is why it is essential to know the most common symptoms of diabetes. Unfortunately, many of these symptoms can develop slowly over time and go unnoticed. The person with diabetes thinks these symptoms are a natural part of aging. Let’s look at the top seven symptoms associated with diabetes.
Frequent Urination
When glucose levels are higher than usual, the kidneys must work harder to filter the excess sugar from the bloodstream. As the kidneys filter glucose out of the bloodstream, the body expels it through urination. Because the kidneys are working double time, the frequency of urination will increase. If you notice urinating more frequently, try increasing your water consumption. It may sound counterintuitive, but it will help flush the excess glucose from the body and reduce the pressure on your kidneys.
Excessive Thirst

If you feel like you are constantly thirsty or suffer from dry mouth, it can be a sign of diabetes. People with diabetes often experience frequent urination, dry mouth, and excessive thirst, which go hand in hand. When you have diabetes, excess glucose builds up in your bloodstream. As the kidneys remove glucose from the body into your urine, it takes fluids from your tissues, which causes you to become dehydrated. Dehydration leaves you thirsty. As you begin to drink fluids, you will quench your thirst; however, you will urinate more and more.
Extreme Fatigue
If your diabetes is left untreated, you will begin to experience extreme fatigue. High glucose levels impair the body’s ability to convert glucose into energy. Furthermore, as the kidneys filter glucose out of the bloodstream, they will also pull nutrients from the body, which can cause you to feel fatigued. Moreover, the dehydration experienced with diabetes can leave your limbs feeling tired and heavy.
Constant Hunger
Because your body continually excretes excess glucose, the nutrients in your foods are leached out and expelled through urination. Because the body cannot properly utilize glucose for energy, it does not receive the fuel it needs, causing you to feel hungry. You may begin to notice that although you eat large amounts of food, your weight remains steady.
Numbness and Tingling
Untreated diabetes can cause nerve damage. Elevated glucose levels combined with elevated triglycerides may damage the nerves in your extremities. This damage can cause a burning sensation, numbness, and tingling in your hands and feet, often referred to as peripheral neuropathy.
Blurred Vision
When glucose levels remain elevated, the body pulls fluids from all tissues, including the eyes. As the eyes become dehydrated, vision can become blurry. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, it is vital to get annual eye exams. Ignoring changes in your eyesight and blurred vision can lead to long-term issues, including vision loss and even blindness.

Slow Healing
If you have undiagnosed diabetes, you may notice that bruises and cuts take a long time to heal. Bladder infections, along with vaginal infections, increase in frequency. Increased glucose levels in the bloodstream can interfere with the body’s natural healing process. As glucose levels rise, it causes systemic inflammation, which can interfere with the immune system, resulting in increased infections and slow healing.
Getting a correct diagnosis can help prevent further damage to the body. If detected soon enough, it may also help manage type 2 diabetes. Eating a healthy diet, getting at least 30 minutes of exercise daily, practicing stress relief techniques, and getting seven hours of sleep each night can help reduce the risk of developing diabetes symptoms. Work towards a healthy body weight by including cardiovascular and strength training to help reduce glucose levels and improve overall health.