index
Chronic inflammation is extremely dangerous and is associated with most chronic diseases. When the immune system is activated, it sends inflammatory cells to help protect and heal damaged tissue. When the immune system becomes overactive, it can continue to send inflammatory cells long after an illness or injury, resulting in chronic inflammation. The symptoms of chronic inflammation are as varied as the cells, tissues, and organs in the body.
Inflammation is the first line of defense against illness or injury. The inflammatory response traps dangerous bacteria, protects injured tissues, and begins healing. When the body becomes confused, inflammation can continue long after wounded tissues have healed or illness has passed.
Chronic Inflammation Symptoms
Chronic inflammation can be challenging to spot as the symptoms can mimic other health conditions, infections, and injuries. Here are the top symptoms of chronic inflammation:

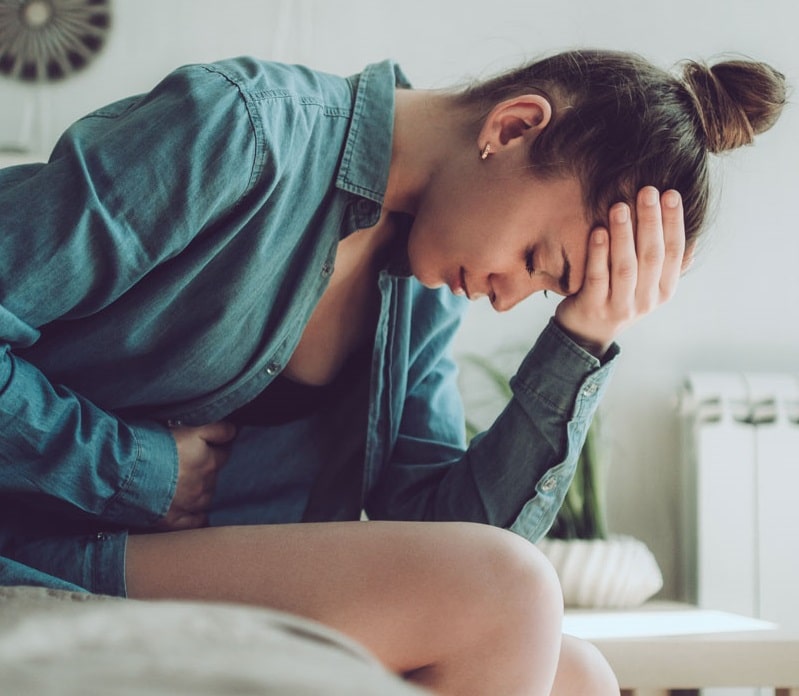
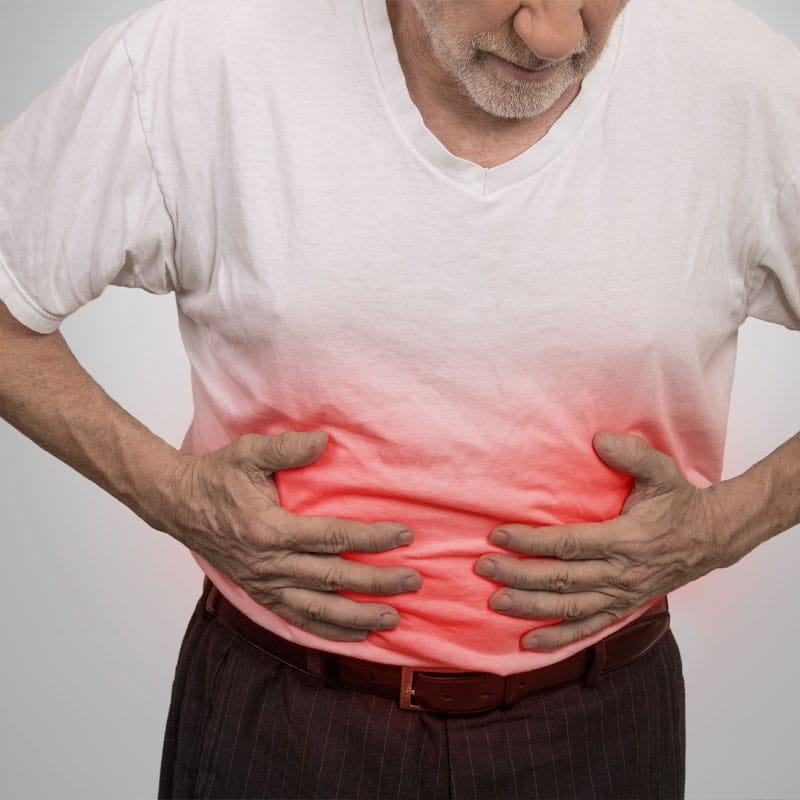
- Abdominal Pain—Chronic inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract can cause several digestive woes, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, bloating, and gas. Additionally, inflammation can damage the tight junctures in the intestines, resulting in leaky gut syndrome, which allows toxins and bacteria to leak out of the digestive system and into the body.
- Chest Pain—Chronic inflammation of blood vessels, lung tissues, and the muscles in the chest wall can all lead to chest pain. When blood vessels become inflamed, they restrict blood flow, which can lead to angina. When the lining of your lungs becomes inflamed, it can cause pleurisy, which causes pain upon inhalation and exhalation. Finally, inflammation of the chest wall, also known as costochondritis, can cause chronic inflammation symptoms that mimic a heart attack. The pain can be sudden and severe.
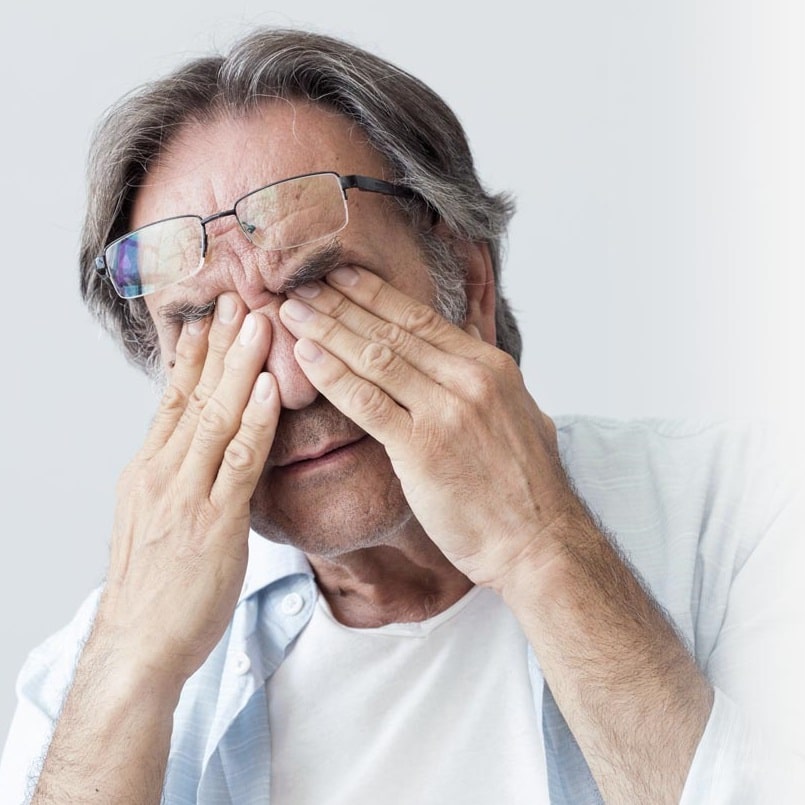
- Cognitive Issues—Inflammation can impact brain health, resulting in memory, emotional, and learning difficulties. It can also affect the body’s ability to make neurotransmitters, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
- Fatigue—If you are continually tired even after a whole night’s sleep, you may suffer from chronic inflammation. Long-term inflammation can cause you to feel run down like you do when you are sick. Long-term systemic inflammation increases the need for cellular energy as the body produces more immune cells, which deplete your energy stores and cause fatigue.

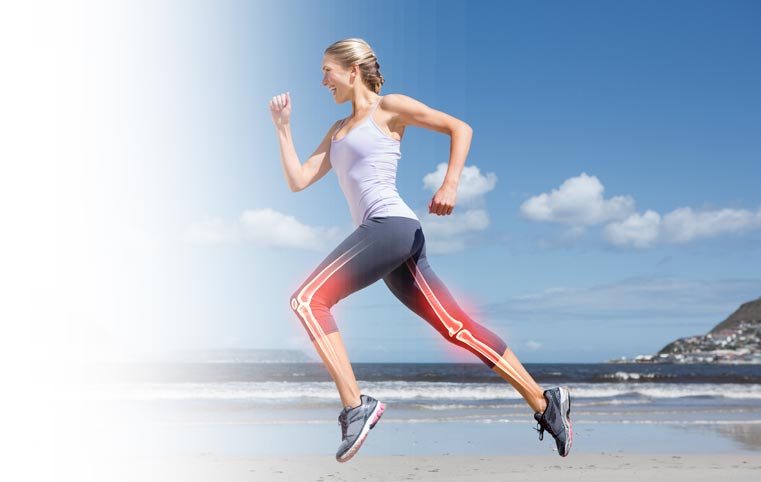
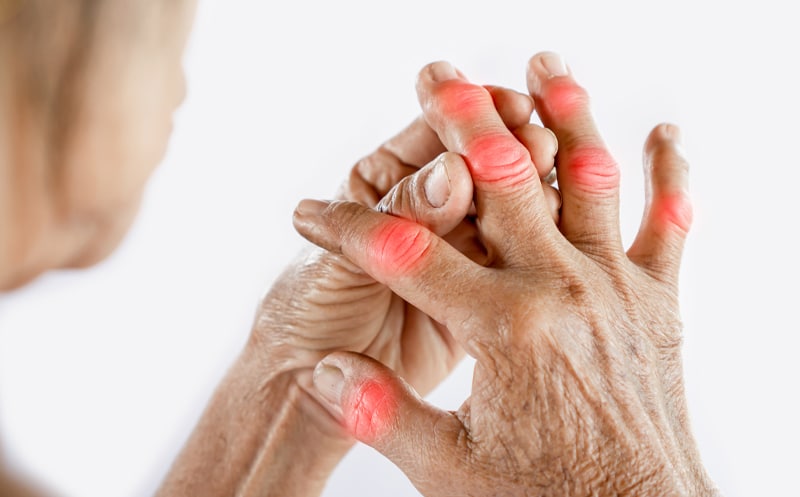
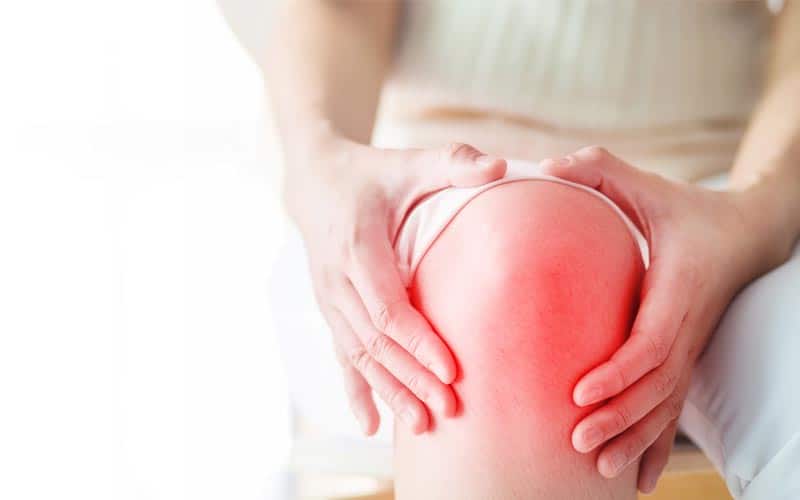
- Joint Pain and Stiffness—Systemic inflammation causes body pain, including joint pain and muscle stiffness. When inflammation occurs, the immune system releases inflammatory cytokines to fight disease. Unfortunately, these cytokines attack your muscles and joints, causing pain, swelling, and redness.
- Phlegm—Are you constantly blowing your nose or clearing your throat due to thick phlegm? Chronic inflammatory response syndrome causes inflammation in the respiratory system. The body produces phlegm to protect the respiratory system’s epithelial cells from further damage.
- Skin Rash—The signs of inflammation can extend to the skin. Inflammatory skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis create red, flaking, and rough skin. These conditions are mainly due to an overactive immune system and systemic inflammation.
Common Inflammatory Diseases
Inflammatory diseases occur when there is ongoing inflammation throughout the body. Here are the most common chronic conditions associated with systemic inflammation.

- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Asthma
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Crohn’s Disease
- Eczema
- Endometriosis
- Fatty Liver Disease
- Graves’ Disease
- Gout
- Hepatitis
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Obesity
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Peptic Ulcer
- Periodontitis
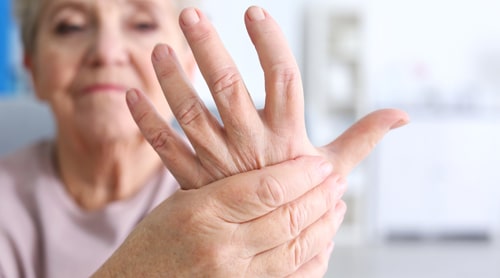
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Scleroderma
- Sinusitis
- Sjogren’s Syndrome
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Tuberculosis
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Ulcerative Colitis
- Vasculitis
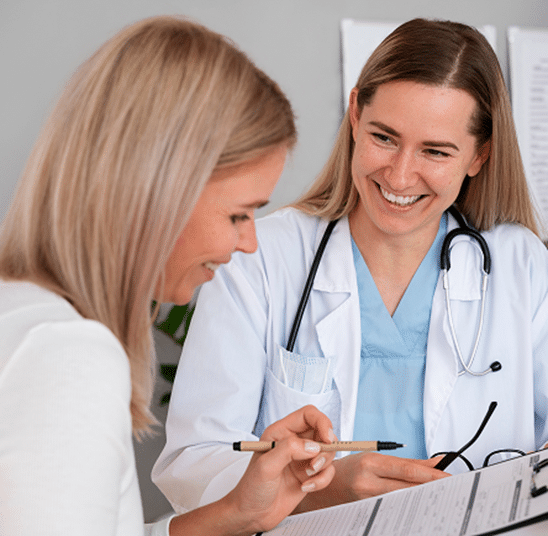
Testing for Chronic Inflammation
Testing for chronic inflammation requires a multipronged approach. Your functional medicine doctor will begin by taking a complete health history that includes your lifestyle choices, family history, symptoms, and prior diagnoses. Some common blood tests used include:
- High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein—High Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP) is a type of protein that the body produces in response to inflammation. After an injury or an infection, high sensitivity C-reactive protein indicates the inflammatory response is activated.
- Sedimentation Rate—The sedimentation rate, abbreviated ESR, measures how fast red blood cells settle in a blood sample. Typically, sedimentation occurs slowly, but inflammation causes the red blood cells to settle quickly. Therefore, an elevated sedimentation rate may indicate inflammation.
- White Blood Cell Count—This test measures your white blood cells. If they are high, it indicates the immune system is activated. When the immune system is activated, it causes an inflammatory response.
Each test examines different parts of the blood to see if they show signs of inflammation. Unfortunately, these tests cannot tell where the inflammation is coming from; however, they indicate whether inflammation is present in the body. Furthermore, these tests, run over time, can help determine whether inflammation worsens or resolves.
Holistic Treatment for Chronic Inflammation
There are many natural ways to reduce and relieve chronic inflammation. Each method helps to calm the immune system, improve your health, and reduce systemic inflammation. Here are our top recommendations on the best holistic way to reduce chronic inflammation:

- Exercise—150 minutes of exercise each week can help reduce inflammation naturally. Additionally, moderate exercise improves immune function.
- Food Sensitivities—If you have any food sensitivities, consuming them will cause you to experience inflammation. Follow an elimination diet and learn which foods may be causing your inflammation. Then, avoid them to prevent inflammation.
- Inflammatory Foods—Knowing which foods are pro-inflammatory (sugar, refined carbohydrates, simple carbohydrates, and dairy products) and removing them from your diet can help reduce inflammation. Replace the foods with anti-inflammatory foods like fresh herbs, vegetables, fatty fish, and fresh fruits.
- Stress Relief Techniques—Chronic stress has been linked to chronic inflammation. Stress relief techniques such as yoga, deep breathing exercises, journaling, meditation, and prayer can help reduce stress and relieve inflammation.
- Supplementation—Several supplements can help to fight long-term inflammation. Adding fish oil, turmeric, and probiotics to your supplementation program can help relieve the inflammation in your body.
Researchers link inflammation to almost every chronic disease. Learning to spot the signs and symptoms of inflammation and relieve systemic inflammation is the first step toward improved health. If your body has become inflamed, talk with a functional doctor who understands how to heal it naturally. To reduce inflammation, you should also adopt an anti-inflammatory diet, get the recommended amount of exercise, get a good night’s sleep, and practice stress relief techniques.