Index
Most people have heard the term autoimmune disease; however, many do not understand the depth and breadth of this diagnosis. Autoimmune diseases impact every area of life and often cause inflammation, widespread pain, fatigue, and a plethora of other symptoms.
What are autoimmune diseases, and how do they impact your health? Autoimmune diseases occur when the immune system erroneously thinks your healthy cells are foreign invaders like bacteria and viruses. Usually, when these germs enter the body, the immune system sends out immune cells to fight these microbes to help prevent illness and disease. The immune system begins attacking healthy cells, causing damage to tissues and organs that results in diseases like systemic lupus, type 1 diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis.

Risk Factors for Autoimmune Diseases
Researchers are unsure why the immune system sometimes attacks healthy cells. However, some people are at an increased risk of developing autoimmune diseases compared to others. Common factors that increase the risk of developing autoimmune diseases include-
- Sex
Women are 50 percent more likely to develop autoimmune disease symptoms than men. The risk increases even more during a woman’s childbearing years (15 to 44 years old).
- Ethnicity
Certain ethnic groups are at an increased risk of developing certain autoimmune disorders. For example, Hispanics and African Americans are more likely to develop lupus than Caucasians.
- Environment
Researchers may link the increased incidence of autoimmune disorders to environmental factors. They are trying to determine whether chemical and solvent exposure or increased infections are involved.
- Diet
The foods you eat may increase your autoimmune risk. Eating processed foods or those high in fats and sugars has been linked to systemic inflammation, which may cause an immune response.
Types of Autoimmune Diseases
There are more than 80 types of autoimmune disorders. Some of the common autoimmune diseases include-
- Arthritis
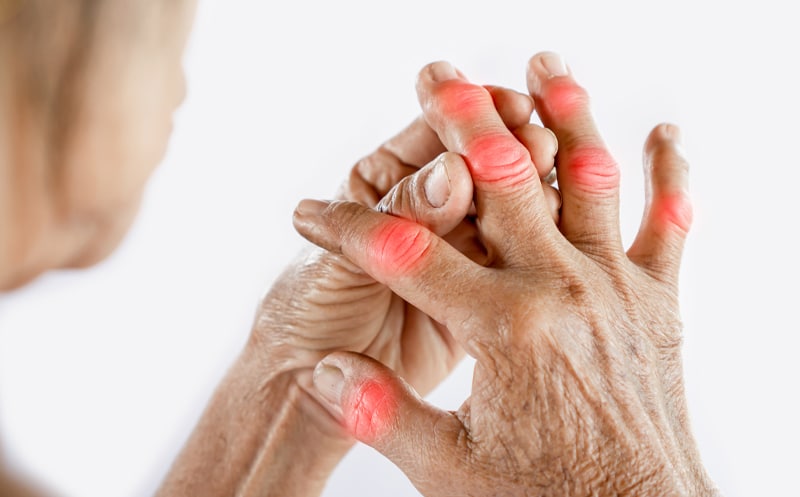
Autoimmune diseases cause both rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. In rheumatoid arthritis, immune cells attack the body’s joints. When this occurs, you will experience stiffness, redness, warmth, and soreness in your joints. Conversely, psoriatic arthritis occurs when skin cells develop too quickly. The overabundance of skin cells can cause stiffness, pain, and swelling of your joints.
- Celiac Disease
Individuals with celiac disease cannot eat foods containing gluten or use products containing gluten, such as cosmetics, medicines, and other items. Consuming gluten activates the immune system, attacking the GI tract.
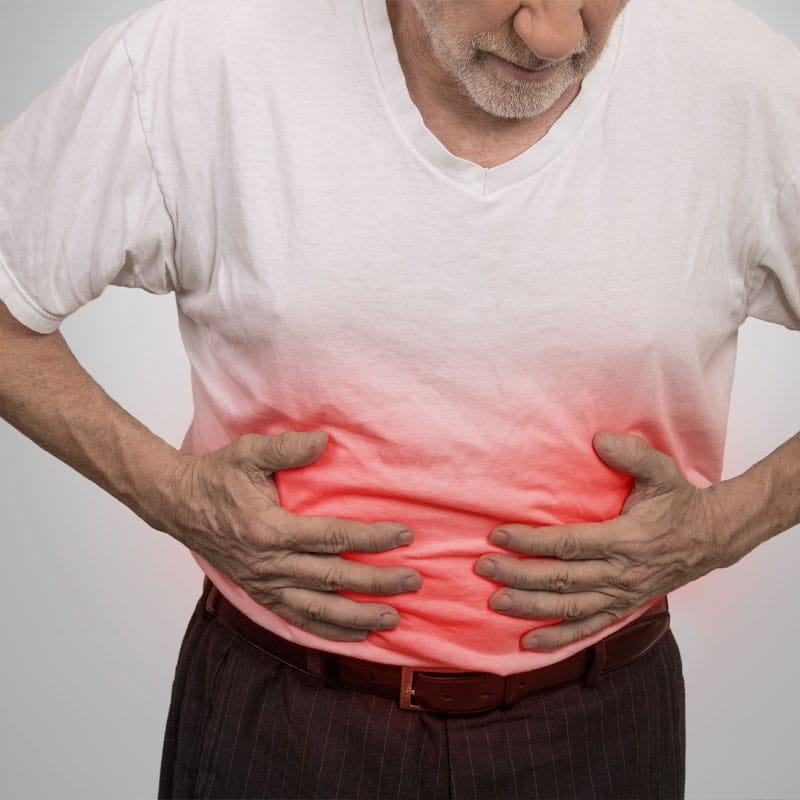
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease encompasses a variety of digestive disorders that inflame the intestinal wall lining. Two of the most common are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. These diseases cause digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, and abdominal pain.
- Multiple Sclerosis
One of the most common signs of lupus is the butterfly rash across the nose and cheeks. Systemic lupus erythematosus also affects the brain, heart, joints, and kidneys, resulting in fatigue, joint pain and swelling, headaches, anemia, hair loss, and more.
- Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. When the body does not produce enough insulin, blood glucose levels increase. High blood glucose levels damage blood vessels and organs like the eyes, heart, and kidneys. Furthermore, nerves can become damaged, leading to neuropathy.

Symptoms of Autoimmune Diseases
The symptoms of autoimmune disorders vary based on the individual disorder; however, some of the most common symptoms include-
- Concentration difficulties
- Digestive issues
- Fatigue
- Hair loss
- Low-grade fevers
- Muscle aches
- Numbness and tingling in the extremities
- Pain
- Redness
- Skin rashes
- Swelling
Diagnosing Autoimmune Diseases
Suppose you are experiencing symptoms of autoimmune diseases. In that case, you should find a doctor who understands how the immune system works and how it impacts the different systems in the body. Our functional medicine doctors embrace the fact that the body has the innate ability to heal itself. Functional medicine seeks to determine the root cause of your illness and then works to correct the problem rather than just treating the symptoms.
Although no single test can diagnose autoimmune diseases, a variety of tests, a detailed family history, and a physical examination can help. Autoimmune doctors will also discuss symptoms, how long the symptoms have been present, diet, and lifestyle choices. This information will help the doctor determine if you have an autoimmune disease.

Holistic Treatment for Autoimmune Disease
Treating autoimmune diseases requires a multipronged approach that addresses the symptoms you are experiencing and supports the immune system so it can function correctly. Your autoimmune disease treatment plan may also include steps to provide immediate relief and work to correct imbalances to promote your health. Some standard methods include an immune system booster, an autoimmune protocol diet, and a variety of healthy lifestyle choices that provide immune support.
- Autoimmune Protocol Diet
An autoimmune protocol diet reduces inflammation and relieves pain and the symptoms of autoimmune diseases like celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus. The diet eliminates pro-inflammatory foods like gluten, peanuts, nightshade vegetables, dairy products, processed foods, refined sugars and carbohydrates, artificial sweeteners, food additives, alcohol, caffeine, and eggs. They replace these items with whole foods like lean proteins, healthy fats, probiotic-rich foods, natural sweeteners, fresh fruits, and vegetables.
- Exercise
Plenty of exercise, including aerobic activity, strength training, and flexibility exercises, helps reduce inflammation and promote health. You should exercise at least 30 minutes daily to improve your overall health, flush toxins from the body, and naturally enhance the immune system. At first, it can seem impossible to exercise for half an hour each day; however, once you begin experiencing the positive effects of exercise, you will wonder why you didn’t start years earlier.
- Hydration
Proper hydration supports the immune system. Lymph fluid, primarily water, carries immune cells throughout the body. When you are dehydrated, your immune system can become impaired. Adequate water intake based on weight and activity levels enhances the immune system.
- Immune System Booster
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system no longer functions properly. Instead of attacking dangerous microbes like viruses and bacteria, they attack healthy cells, organs, and tissues. An unhealthy, weak immune system will not function properly, so an immune booster may help correct immune disorders.
- Sleep
Sleep is vital to your health. When you sleep, your body recovers, produces hormones, consolidates memories, and creates infection-fighting substances. Getting between 7 and 9 hours of sleep boosts your immune system.
- Stress Relief
Researchers have associated chronic stress with systemic inflammation and an increased risk of illness and disease. Incorporating stress relief practices into daily life can lower stress levels, improve health, and boost immunity. Top techniques include daily journaling, yoga, meditation, and deep breathing.
Our functional medicine doctors understand how to boost your immune system, address underlying health problems, and utilize the body’s natural ability to heal itself. Some treatment protocols for autoimmune diseases include immune-boosting techniques like diet, exercise, stress relief, detoxification, and proper hydration. These methods help to reduce inflammation, correct problems in the immune system, and treat autoimmune disorders.