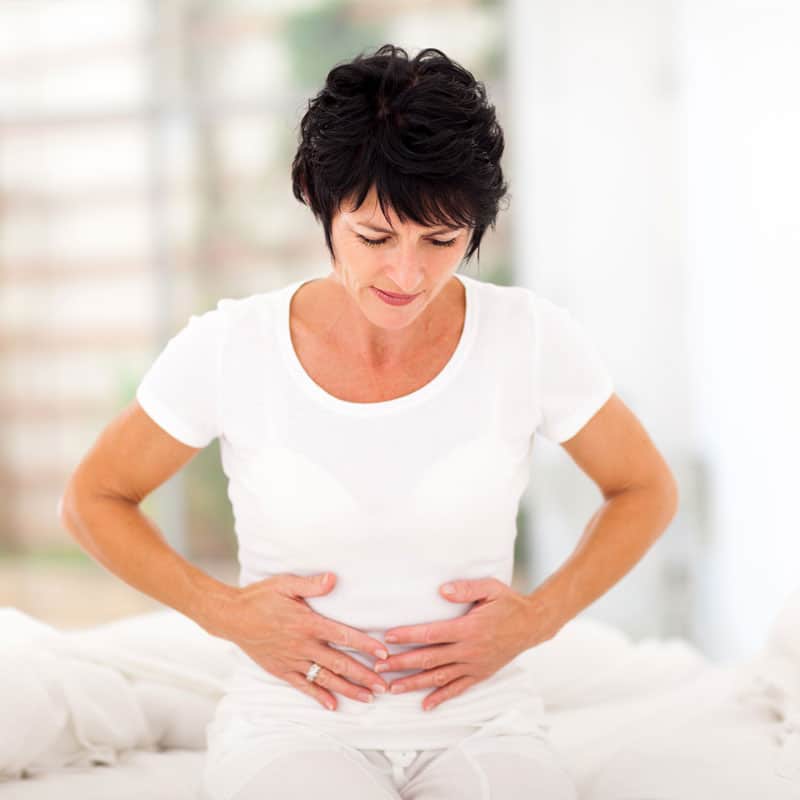
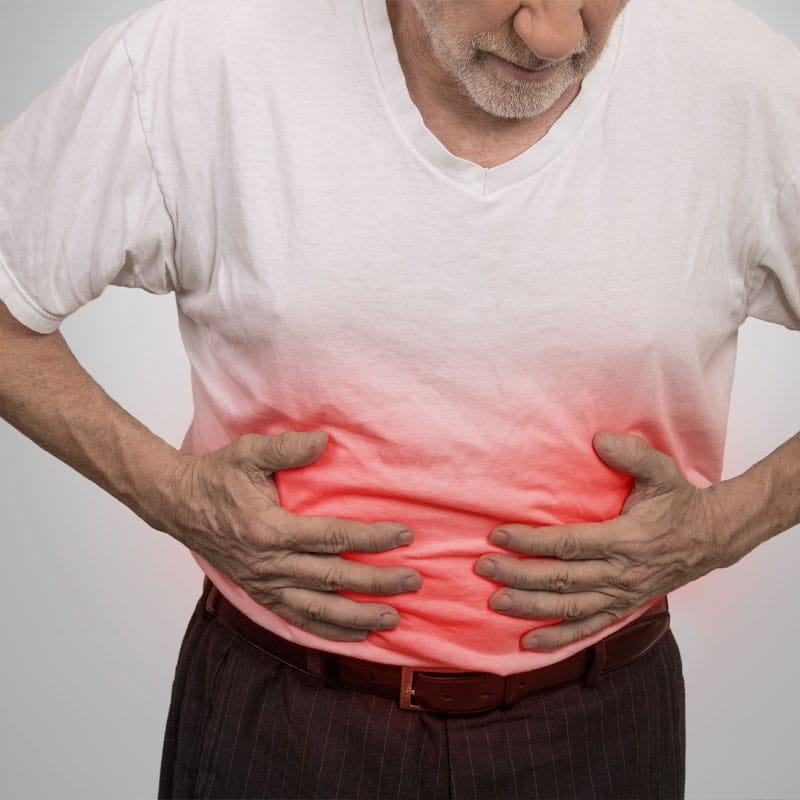
Most people complain of being bloated at one time or another. Oftentimes, we use this term when we feel full or have over eaten; however, it can also occur regularly and be a sign of an underlying chronic condition. Bloating causes the stomach to feel tight and full. It is often described as a feeling of fullness, tightness, or swelling in the belly and can cause your abdomen to become distended, painful, or hard. Many people relate the visual signs of bloating to being 7 months pregnant. It is often accompanied by excess gas, abdominal gurgling, frequent belching, or pain.
Causes of Bloating
The most common causes of bloating include-
- Gas trapped in the abdomen or gastrointestinal tract. Gas builds up in the digestive tract when you swallow a lot of air, food sits in the stomach for an extended period of time, or when undigested food particles are not broken down properly. Although everyone swallows air as they eat or drink, certain individuals swallow more air because they eat or drink too quickly, they smoke, their dentures are loose, or they chew gum. This can lead to excess gas or gas pain.
- Digestive issues, including irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, and food sensitivities can cause bloating. When you are constipated, stool is backed up in the large intestine and causes discomfort. If gas builds up behind this stool, it further exacerbates the symptoms.
- Hormonal changes can also cause bloating. Increased estrogen levels along with low progesterone levels can cause bloating and water retention. Hormones can become imbalanced during perimenopause, pregnancy, or during the monthly cycle.
- Diet – Your daily diet may also lead to bloating or a gassy stomach. Carbonated beverages can increase the amount of gas in the GI tract. Consuming too much sugar or salt can also increase inflammation and water retention. Finally, not consuming enough fiber can cause constipation which can lead to discomfort.
Tips to Reduce Bloating
There are many things that you can do to help relieve the pressure and pain associated with bloating. Understanding why you are bloated is the first step to relieving this discomfort. Here are some examples.
- Drinking Water – Constipation is one of the most common digestive complaints. This uncomfortable digestive woe can increase bloating and discomfort. You can counteract constipation by increasing your consumption of soluble fiber and drinking more water. In addition to this, increasing your physical activity can improve gut motility and reduce constipation.
- Digestive Enzymes – If your body is not producing the necessary enzymes needed to digest your foods properly, it can cause bloating, gas, water retention and abdominal discomfort. Digestive enzymes help the body break down carbohydrates and provide relief to your most troublesome digestive woes. Foods that naturally contain high amounts of digestive enzymes include pineapple, papaya, cilantro, and parsley.
- Fiber – Foods that are high in fiber can produce a lot of gas. Some of the main offending high fiber foods that cause bloating are lentils, whole grains, and beans. Furthermore, fatty foods can slow down your digestion and delay the emptying of your stomach. Although this can increase your satiety, it can also cause bloating. On the other hand, increase your consumption of soluble fiber.
- Food Intolerances – Food allergies and food intolerances are quite common. When you consume foods that you have a sensitivity to, it can lead to excessive gas or bloating. Consider keeping a food diary to determine the foods causing you gas. Eliminate the most offending foods from your diet including dairy products, eggs, and gluten.
- Low FODMAP Diet Foods – Irritable bowel syndrome causes a number of symptoms including gas, abdominal pain, discomfort, diarrhea, constipation, and bloating. Decreasing your consumption of high FODMAP foods like onions, garlic, wheat, beans, pears, apples, and cruciferous vegetables may help to decrease bloating. Increase your consumption of low FODMAP foods like bananas, blueberries, grapefruit, bok choy, celery, carrots, grains, nuts, seeds, and most eggs.
- Peppermint Oil – If your bloating is due to the altered function of your digestive tract muscles, peppermint oil may help. It acts as an antispasmodic that can reduce the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, including bloating, gas, and constipation.
- Probiotics – Your digestive tract is filled with bad and good bacteria, yeasts, and fungi. When the gut becomes imbalanced, it can lead to increased gas production. If you are experiencing bloating, gas, and other digestive problems, a probiotic supplement can help. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help balance the bacteria in the digestive tract.
- Swallowing Too Much Air – Swallowing too much air or ingesting carbonated beverages can increase the risk of bloating. Carbonated beverages are made with carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is a gas that is released from the drink once it reaches your stomach, increasing the amount of air and gas in the GI tract. In addition to this, you can swallow too much air when you chew gum, drink through a straw, eat too fast, or talk while eating.
- Walking – Walking and other physical activity can help regulate your bowels, which can help reduce excess gas and bloating. Try taking a walk after meals to help improve digestion.
- Yoga – Yoga has been shown to position the abdominal muscles to help relieve trapped gas in the gastrointestinal tract, which can help reduce abdominal bloating. Performing squats, the child’s pose, and the happy baby pose can help improve your digestive health naturally.
Ready to Improve Your Digestive Health?
Bloating is typically caused by excess air trapped in the gastrointestinal tract. It can cause abdominal pressure, swelling, and pain if left unchecked. Preventing bloating requires understanding the cause of your symptoms. If you are experiencing mild bloating symptoms, increase your activity levels, drink more water, and eat more fiber. If your bloating symptoms persist, it can signal a more serious medical issue. Our functional medicine practitioners can help find the root cause of your bloating and improve your gut health.