Caffeine naturally occurs in many types of plants. It stimulates the central nervous system and helps 
Caffeine and Calcium Excretion
Caffeine can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb and metabolize calcium, which can contribute to osteoporosis. Additionally, too much caffeine can cause muscle twitches, muscle spasms and an increased incidence of fractures.
Stress Hormones and Caffeine Usage
The stress hormone cortisol is produced in the adrenal glands. This hormone is responsible for blood sugar regulation, the regulation of blood pressure and a plethora of other function. However, when you have too much cortisol in the body, inflammation can occur.
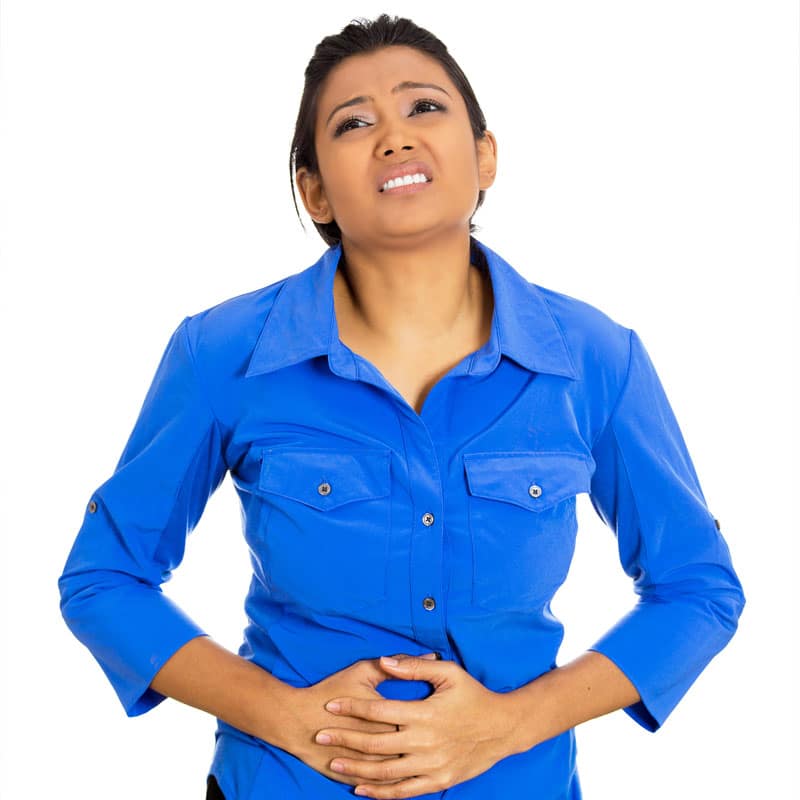
Caffeine, the Digestive Tract and Abdominal Pain
Caffeine increases the amount of hydrochloric acid in the stomach and can cause heartburn, upset stomach, nausea, diarrhea and vomiting. Caffeine can irritate the lining of the digestive tract, including the stomach and small intestine. When this occurs you can experience abdominal cramps, pain and elimination problems. If you suffer from digestive problems, limiting your intake of caffeine can help lower the acid in the stomach and may help relieve many of your digestive woes.
Caffeine and Inflammation and Fatigue
Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase energy levels; however, this affect only lasts for a short time. When the caffeine leaves the body, your energy levels will wane and cause you to experience fatigue. In order to increase energy levels, most people reach for another caffeinated beverage, which starts the whole cycle to occur again.
Caffeine can also cause inflammation to occur throughout the body. Caffeine is a diuretic, which causes increased urination. As you urinate more frequently, your body becomes dehydrated. Dehydration can cause inflammation throughout the body. To fight this effect, drink at least 64 ounces of water a day and limit your caffeine intake.
Caffeine Causes Insomnia and Irritability
Anxiety and irritability are two of the most common complaints of caffeine drinkers. When you ingest caffeine, it causes the adrenal glands to release adrenaline. Adrenaline causes the body to become hyper-aroused and allows your emotions to take control of your thought processes, often resulting in irritability and anxiety.
Because of its stimulant properties, caffeine can cause sleeplessness, insomnia and poor sleep. Caffeine can stay in the body for six hours or longer. In order to improve your sleep, set a bedtime and stick to it, avoid caffeine and sleep in a cool room.
Increased Heart Rate Caused by Caffeine

Caffeine Affects Nervousness and Depression
Caffeine can cause a plethora of emotional problems, including nervousness and depression. Caffeine can reduce the amount of restorative sleep you get each night, which can lead to nervousness and anxiety. To help prevent nervousness and sleep deprivation, try limiting your caffeine. However, it is important to slowly decrease the amount of caffeine you ingest because abruptly stopping caffeine can increase the risk of depression, fatigue and irritability.
Ready To Get Energized With a Caffeine Free Diet?
Caffeine can occur either naturally or it can be added to products to enhance the energizing effects of a drink. Drinking too much caffeine can cause a plethora of medical conditions, including and increased heart rate, sleeplessness, depression and inflammation. To protect your health, limit the amount of caffeine you ingest.